Storage is a core component of the data center fabric and is an intrinsic part of Microsoft’s software-defined data center solution. Storage investments are centered on bringing value to customers in terms of increasing cloud scale, availability, performance, and reliability, while lowering acquisition and operational costs – with Windows Server, and now also with Microsoft Azure Stack.
What is Software Defined Storage or SDS ?
The storage industry is going through interesting shifts driven by various factors – large-scale cloud services influencing design points and enabling the use of standard volume hardware by putting more intelligence into storage software. Virtualization is driving the need for mobility and density – containers will push that envelope further. Large levels of scale out ensure that “pay-as-you grow” models are seamless, elastic and fluid.
In simple words – SDS is cloud scale storage and cost economics on standard volume hardware.
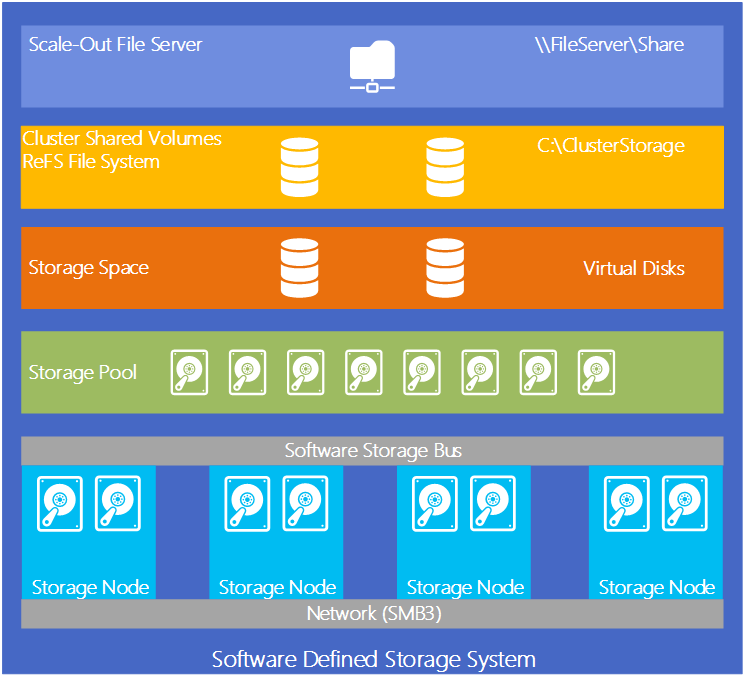
Storage Spaces Direct is in preview in Windows server 2016 which is upcoming server software from Microsoft. Storage spaces direct has the same principle as VMware VSAN – leverages local disks of each host (DAS storage) in order to create a shared pool of clustered storage visible by all the hosts in the cluster. And this shared storage can be presented as a VM’s datastore. Storage spaces direct is an evolution of Storage spaces based on ReFS. The resilient file system (ReFS) and those ReFS formatted volumes used in conjunction with Storage spaces uses striping and data mirroring. ReFS has built in scanner which is used for auto-healing. This proactively running scanner called scrubber which scans the volume for errors periodically in a background and allows proactively monitor the volume for errors and correct them. With Windows Server Technical Preview there is newly introduced Storage Spaces Direct, where you can now build HA Storage Systems using storage nodes with only local storage. Disks devices that are internal to each storage node only (no shared enclosure). The current Windows server 2012 R2 storage spaces in order to provide this function needs shared JBOD which is basically an external enclosure. This will not be needed in Server 2016 and Storages Spaces direct. Storage Spaces Direct uses SMB3 for internal communication. SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel (low latency and high throughput storage).

Storage Spaces Direct enables service providers and enterprises to use industry standard servers with local storage to build highly available and scalable software defined storage for private cloud. Enabling Storage Spaces to use local storage for highly available storage clusters enables use of storage device types that were not previously possible, such as SATA SSD to drive down cost of flash storage, or NVMe flash for even better performance.
The primary use case for Storage Spaces Direct is private cloud storage, either on-prem for enterprises or in hosted private clouds for service providers. Storage Spaces Direct has two deployment modes: private cloud hyper-converged, where Storage Spaces Direct and the hypervisor (Hyper-V) are on the same servers, or as private cloud storage where Storage Spaces Direct is disaggregated (separate storage cluster) from the hypervisor. A hyper-converged deployment groups compute and storage together. This simplifies the deployment model, with compute and storage scaled in lock step. A private cloud storage deployment separates the compute and storage resources. While a more complex deployment model, it enables scaling compute and storage independently and avoids over provisioning.
A server with local storage contains internal storage devices in the chassis, in a storage enclosure physically connected only to that server, or a combination of these. This contrasts our current model in Windows Server 2012 R2, where storage devices must be in one or more shared SAS storage enclosures and the enclosure must be physically connected to all servers in the highly available cluster.
Source: Microsoft Blogs